Brain
-
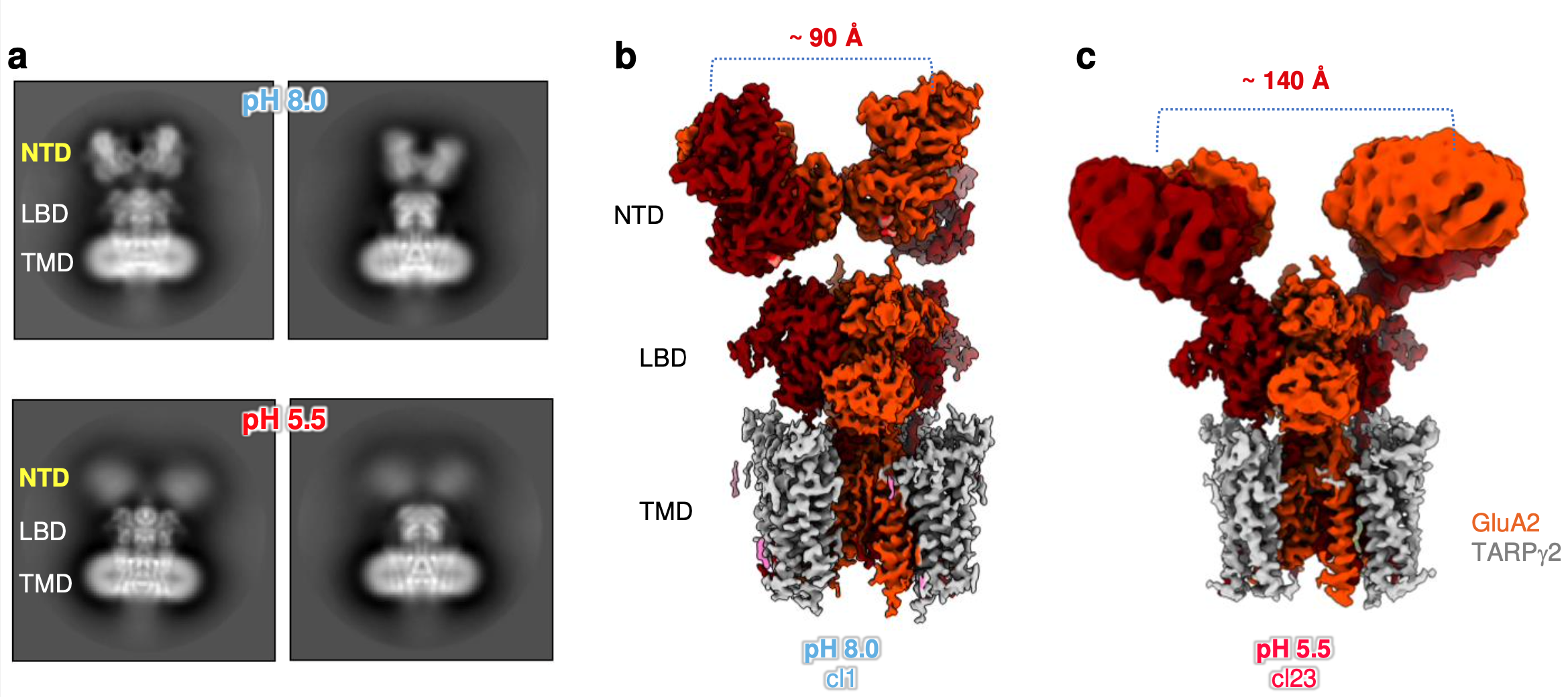
Research Snapshot: Protons can tune synaptic signaling by changing the shape of a protein receptor
Research from Teru Nakagawa, professor of molecular physiology and biophysics, describes intricacies of normal brain function with implications for our understanding of brain injury and recovery: A decrease in pH can modify a neurotransmitter receptor’s structure, thereby modulating its location and kinetics. Read MoreAug 14, 2024
-

VUMC scientists record powerful signal in the brain’s white matter
Vanderbilt researchers report that when people who are having their brains scanned by fMRI perform a task, like wiggling their fingers, certain signals increase in white matter throughout the brain, which has long been thought to play a lesser role the more the brain's more energetic gray matter. Read MoreOct 16, 2023
-

White matter and psychosis
The microstructure of white matter in the brain could be an important risk marker for psychosis, Vanderbilt researchers have discovered. Read MoreJan 27, 2022
-

Researchers create technique that corrects distortions in MRI images
Perfecting MRI images with deep learning, Vanderbilt and VUMC researchers have created a technique that corrects image distortions, which provides more accurate information for researchers, radiologists and neuroscientists to better interpret brain scans. The work by Bennett Landman, professor of electrical engineering and computer science and radiology and radiological sciences, and Kurt Schilling, research assistant... Read MoreNov 11, 2020
-

Histamine circuits in brain reward center
Histamine — commonly associated with allergies — also has a signaling role in the brain’s reward center and may offer a novel target for treating addiction. Read MoreOct 29, 2020
-

Depression and the brain-age gap
Older depressed adults show accelerated brain aging, according to a new study from Vanderbilt researchers, who suggest that the effects of depression may speed the decline in cognitive functions in older individuals. Read MoreOct 19, 2020
-

Brain blood vessel response to hypoxia
The brain’s response to low oxygen — growth and remodeling of blood vessels — involves certain cell types and molecular pathways, Vanderbilt researchers have discovered. Read MoreOct 15, 2020
-

A connection to schizophrenia
The insula, a small region of the brain involved in diverse brain functions had widespread dysconnectivity in schizophrenia, Vanderbilt researchers found. Read MoreJun 23, 2020
-

Team discovers one more piece to the autism puzzle
Vanderbilt investigators have linked genetic mutations in a single receptor to epilepsy, autism and intellectual disability. Read MoreOct 3, 2019
-

Astrocytes and epilepsy
A protein with important functions in astrocytes — star-shaped brain support cells — may alter neuronal excitability and contribute to seizure activity, Vanderbilt researchers report. Read MoreSep 9, 2019
-

MRI technique detects spinal cord changes in MS patients: study
A Vanderbilt University Medical Center-led research team has shown that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can detect changes in resting-state spinal cord function in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). Read MoreApr 19, 2018
-

Sorry, Grumpy Cat—Study finds dogs are brainier than cats
The first study to actually count the number of cortical neurons in the brains of a number of carnivores, including cats and dogs, has found that dogs possess significantly more of them than cats. Read MoreNov 29, 2017
-

‘Mind’s eye blink’ proves ‘paying attention’ is not just a figure of speech
Vanderbilt psychologists have discovered that when you shift your attention from one place to another, your brain 'blinks'—or experiences momentary gaps in perception. Read MoreNov 21, 2017
-

Regulating anxiety in the brain
Two brain signaling pathways have overlapping functions in regulating anxiety, suggesting that therapeutics aimed at one or the other will impact both. Read MoreApr 28, 2017
-

Protecting the blood-brain barrier
Vanderbilt investigators have discovered how a promising cancer immunotherapy causes brain swelling, findings that could lead to ways to protect brain function while fighting cancers. Read MoreDec 9, 2016
-

Blood-brain barrier on a chip sheds new light on “silent killer”
A new microfluidic device containing human cells that faithfully mimics the behavior of the blood-brain barrier is providing new insights into brain inflammation, the silent killer. Read MoreDec 6, 2016
-

Protein structure and epilepsy severity
Understanding how mutations affect the structure and function of inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors will shed light on the mechanisms underlying some types of epilepsy. Read MoreNov 10, 2016
-

Probing drug abuse circuitry
Vanderbilt researchers have identified cocaine-induced modifications at specific neuronal connections, which could aid the development of new therapies for substance abuse disorders. Read MoreNov 4, 2016
-

Total number of neurons—not enlarged prefrontal region—hallmark of human brain
Research by Associate Professor of Psychology Suzana Herculano-Houzel finds that human intelligence comes from the number of neurons in our brains—and it was the invention of cooking that made neuron development possible. Read MoreAug 9, 2016
-

Study gives new meaning to the term ‘bird brain’
The first study to systematically measure the number of neurons in the brains of birds has found that they have significantly more neurons packed into their small brains than are stuffed into mammalian and even primate brains of the same mass. Read MoreJun 13, 2016