Research
-

Limited Submission Opportunity: Tennessee Arts Commission Arts Project Support and Rural Arts Project Support FY26
Vanderbilt University may submit only one application to the Tennessee Arts Commission Arts Project Support (APS) OR the Rural Arts Project Support (RAPS) program. Read MoreOct 16, 2024
-

Vanderbilt receives award from ARPA-H to focus on improving mental health chatbots
A team at Vanderbilt University Medical Center will address the concerns and hopes surrounding health-related AI chatbots with the aid of a two-year funding award of up to $7.3 million from the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H). Read MoreOct 16, 2024
-
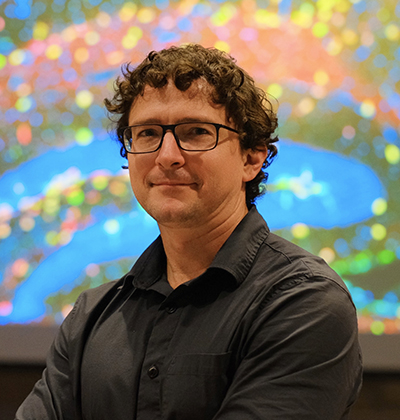

Passion, Perseverance and Synapses: Neuroscientist Richard Sando receives prestigious NIH New Innovator Award
In 2024 the National Institutes of Health awarded Sando a New Innovator Award, part of their High-Risk, High-Reward Research program. This award, which provides $1,500,000 over five years, supports early-career scientists proposing innovative and impactful research that might not get funded in the traditional peer-review process due to its inherent risk. Read MoreOct 11, 2024
-

Limited Submission Opportunity: W.M. Keck Foundation Research Program – Concept Papers (Winter 2025)
Vanderbilt University may submit up to two proposals for the W.M. Keck Foundation Research Program. Read MoreOct 10, 2024
-

Unity Poll: Supermajority reports confidence that their vote will be counted, gains confidence in elections across U.S.
According to this poll, only 10 percent of Americans don’t believe our democracy is in danger, and slightly over 50 percent think it is “under attack.” The rest of the country felt our system was being “tested.” When asked, instead, about “personal freedom,” a similar pattern emerged. In short, there is widespread concern about the state of democracy and personal freedom—themes that have certainly played out on the campaign trail for Vice President Kamala Harris and former President Donald Trump. Read MoreOct 10, 2024
-
Researchers’ study aims to assist scientists in analyzing spatial transcriptomics data
A team of Vanderbilt researchers has released a new benchmarking study that aims to assist scientists in selecting the most effective methods for analyzing spatial transcriptomics data. The study led by Xin Maizie Zhou, assistant professor of biomedical engineering and computer science, evaluates computational tools in spatial transcriptomics innovative technology used to map gene expression patterns in tissues while preserving spatial context. Read MoreOct 10, 2024
-
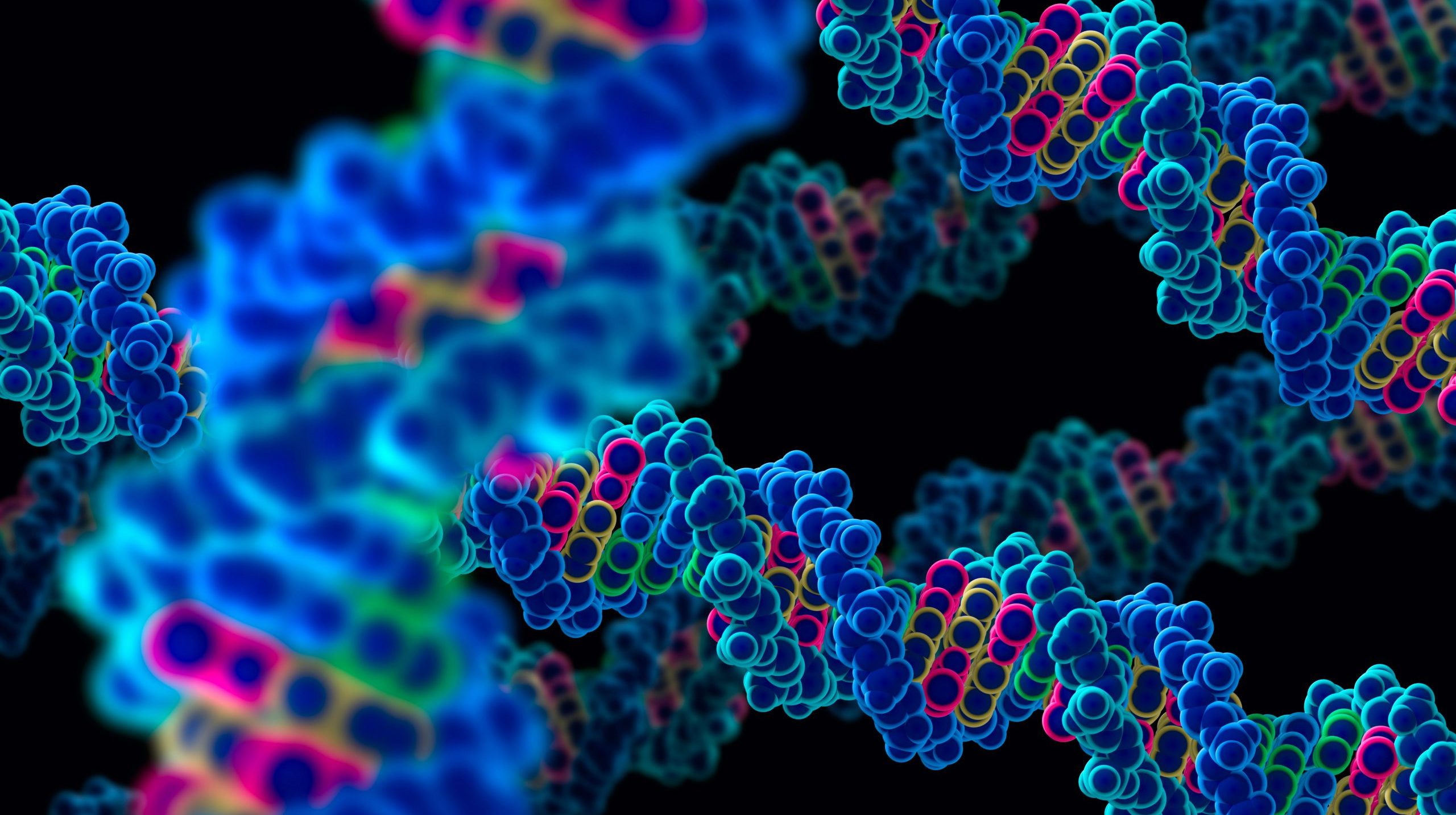

New technology could significantly advance genomic analysis and precision medicine
A team of Vanderbilt researchers has developed a novel tool in the detection and analysis of structural variants in human genomes that could potentially transform genomic analysis and precision medicine. Read MoreOct 10, 2024
-
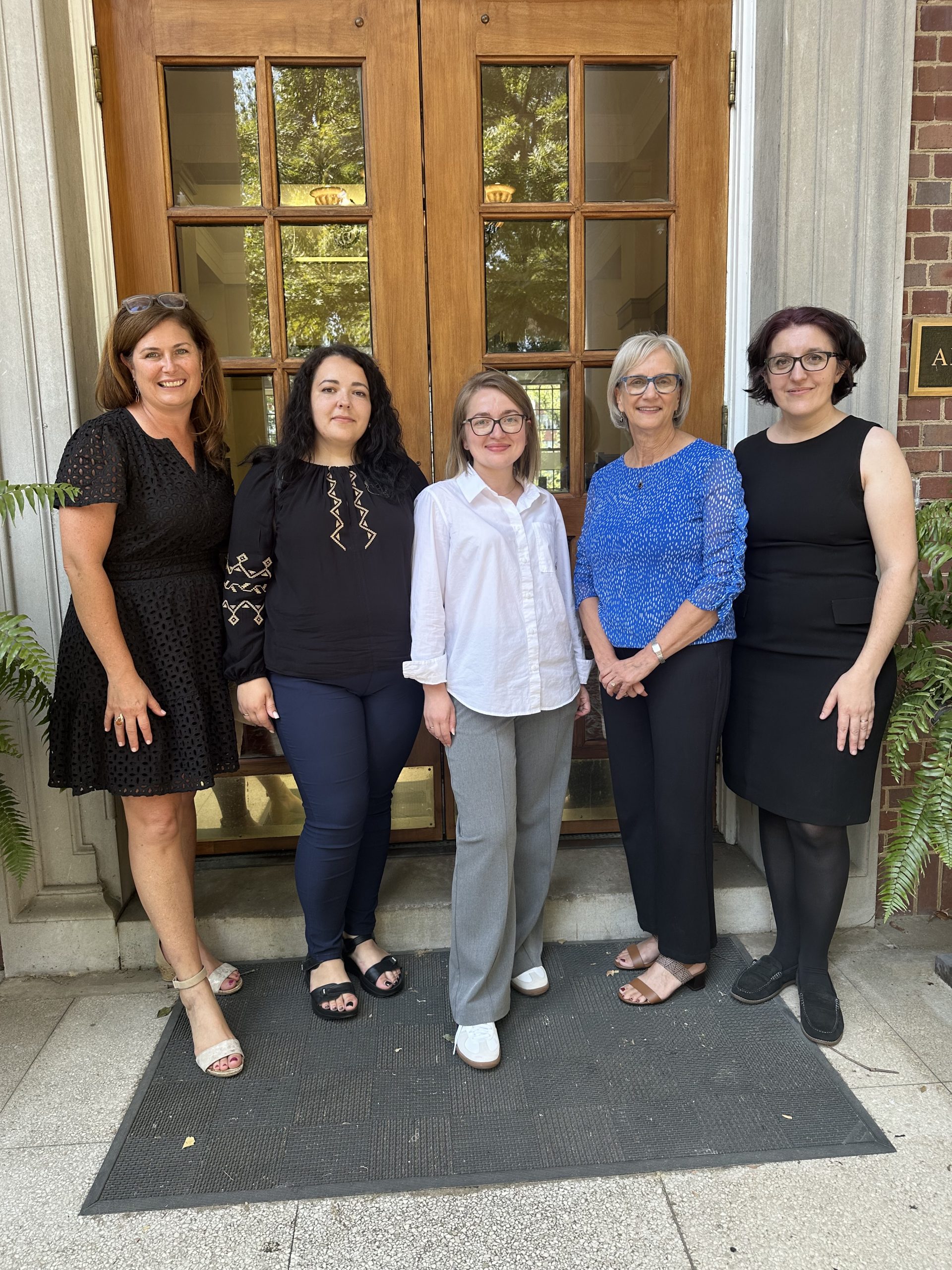

Peabody Global Initiatives hosts delegations from Ukraine, Morocco, and China
In September, Peabody Global Initiatives welcomed visitors from institutions in Ukraine, Morocco, and China to deepen connections and explore opportunities for future collaborations. Peabody Global Initiatives is a new initiative of Vanderbilt Peabody College of education and human development to support faculty to pursue international research and disseminate knowledge,… Read MoreOct 9, 2024
-

New study finds that anesthesia inhibits brain’s predictive processing
A new study led by Andre Bastos, assistant professor of psychology, found that animal subjects under general anesthesia were unable to detect moderate and complex surprises. This discovery deepens the understanding about the nature of consciousness and how it arises. Read MoreOct 8, 2024
-

Kristy Roschke appointed executive director of McGee Applied Research Center for Narrative Studies
Roschke, a renowned expert in media literacy and misinformation, has been named the inaugural executive director of the McGee Applied Research Center for Narrative Studies at Vanderbilt University beginning Oct. 15. Roschke will also hold a faculty appointment in the Program in Communication of Science and Technology in the College of Arts and Science. Read MoreOct 8, 2024
-

2024 MacArthur Fellow Keivan Stassun: Reaching for the stars while raising others up
See how a passion to help underrepresented students ignited astrophysicist Keivan Stassun’s mission, earning him a MacArthur “genius” award. Read MoreOct 7, 2024
-

Dean Krishnendu Roy advocates for increased NIH funding in Washington, D.C.
Krish Roy, Bruce and Bridgitt Evans Dean of the School of Engineering, recently engaged in a leadership roundtable in Washington, D.C. with NIH Director Dr. Monica M. Bertagnolli. Hosted by United for Medical Research (UMR), the forum addressed critical issues in biomedical research funding and efforts to secure sustained federal investments in this vital area. Read MoreOct 4, 2024
-
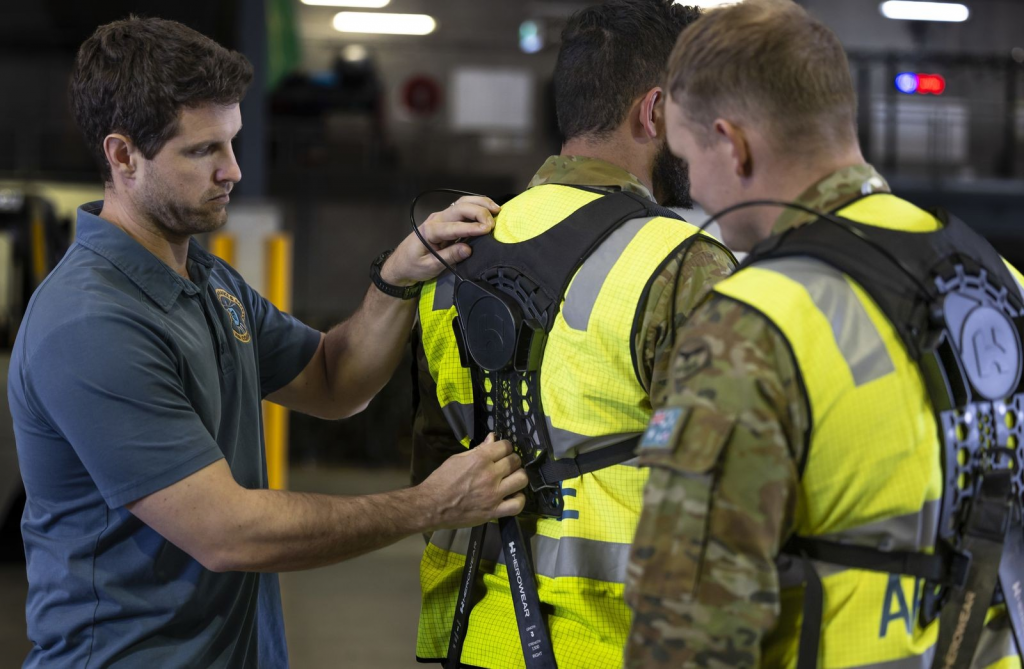

Royal Australian Air Force rolls out hundreds of exosuits created by Vanderbilt spin-off company to reduce back injuries
A back-relieving exosuit designed by HeroWear, a Nashville-based workforce wearable technology company, was co-founded by Karl Zelik, associate professor of mechanical and biomedical engineering and physical medicine and rehabilitation, and two alumni, is continuing to show its effectiveness with the Royal Australian Air Force ordering hundreds of additional suits and eyeing larger expansion. Read MoreOct 3, 2024
-

Erin Calipari wins Society for Neuroscience 2024 Outstanding Career and Research award
Erin Calipari, director of the Vanderbilt Center for Addiction Research and associate professor of pharmacology and molecular physiology and biophysics, has been recognized with the Society for Neuroscience’s 2024 Jacob P. Waletzky award. Read MoreOct 3, 2024
-

Limited Submission Opportunity: Oak Ridge Associated Universities Innovation Partnerships Program FY25
Vanderbilt (VU and VUMC, collaboratively) may submit two applications to the Oak Ridge Associated Universities (ORAU) Innovation Partnerships Program. Read MoreOct 2, 2024
-
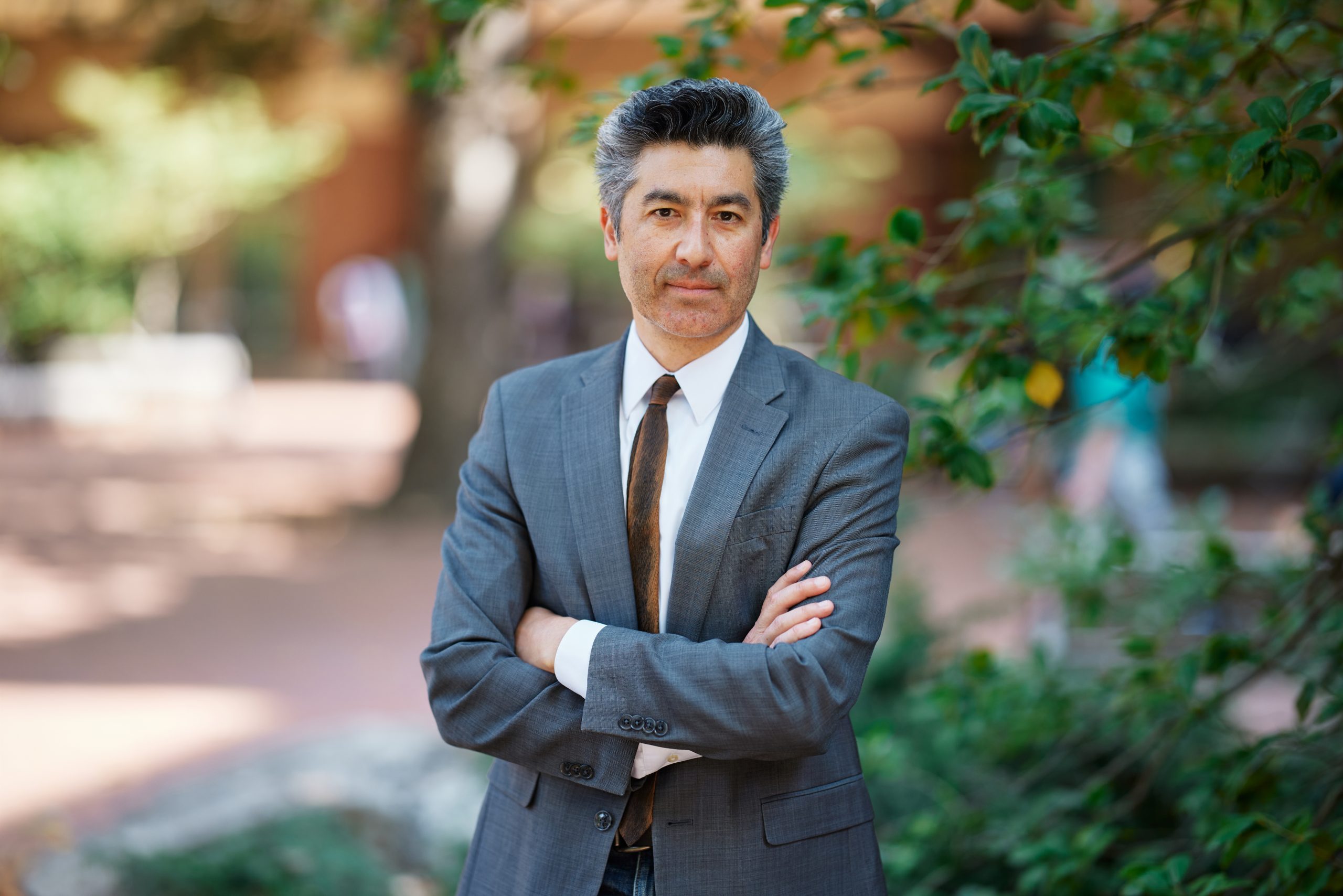

Vanderbilt’s Keivan Stassun named 2024 MacArthur fellow
Stassun, who is also a founding co-director the Fisk-Vanderbilt Master’s-to-Ph.D. Bridge Program, was among the 2024 MacArthur fellows announced on Tuesday, Oct. 1. The fellowship, which is awarded by the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, aims to identify extraordinarily creative individuals with a track record of excellence in a field of scholarship or area of practice. Recipients also demonstrate the ability to affect society in significant and beneficial ways through their pioneering work or the rigor of their contributions, according to the foundation. Read MoreOct 2, 2024
-
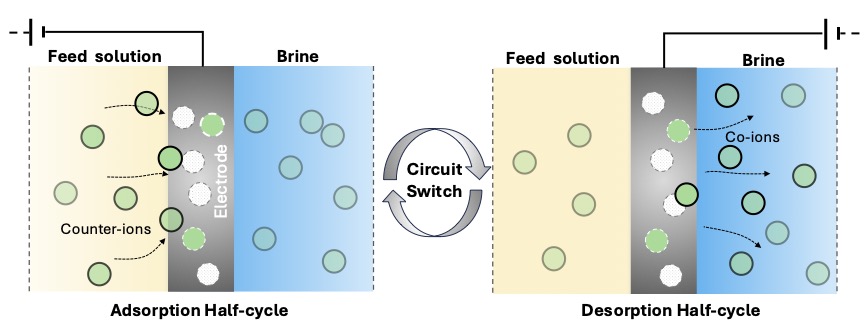
Innovative research unlocks potential of electrochemical separation for water treatment and resource extraction
A team of Vanderbilt researchers have developed novel technology called electrochemical ion pumping that could revolutionize the treatment of water and resource extraction. Read MoreOct 1, 2024
-

Evolved in the lab, found in nature: Uncovering hidden pH sensing abilities
In a groundbreaking study led by Sarah Worthan, Ph.D., a postdoctoral researcher in the Behringer Lab at Vanderbilt University, scientists have successfully evolved microbial cultures that possess the ability to sense pH changes, enabling rapid responses to environmental fluctuations. Read MoreOct 1, 2024
-

Vanderbilt co-authored study of multinational enterprises in China wins prestigious journal award
By Jenna Somers A 2023 study of cultural intelligence in multinational enterprises in China recently won the Basu Sharma Best Paper Award, presented annually for the best publication in the Journal of Comparative International Management. The study, “Cultural Intelligence, Diversity Climate, and Employee Behavior: A Study of MNE Subsidiaries… Read MoreSep 30, 2024
-

Toward inclusive math education: insights from Black students may support more effective teaching strategies
By Jenna Somers A recent study finds that Black high-school students tend not to believe that their teachers are adequately prepared to teach them math in appropriate ways, have negative perceptions of their math ability, and lack awareness about the intersection between math and their desired careers. Published in… Read MoreSep 30, 2024