Health And Medicine
-

Researchers discover method to make traditional topical antibiotic safe to inject, potentially reducing antibiotic resistance
Ointments like Neosporin contain the antibiotic neomycin, which works great to kill bacteria on the outside of the body when you scrape your knee or have a hangnail. But inside the body, neomycin does more harm than good—kidney and neurological damage and deafness. Research Assistant Professor Bhawik Jain and colleagues in his lab have figured out why that is, and how to stop it. This could make neomycin another tool in the fight against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Read MoreOct 10, 2025
-
DelGiorno lands prestigious American Cancer Society award to study therapeutic vulnerabilities in pancreatic cancer
Kathleen DelGiorno, assistant professor of cell and developmental biology, has received a Research Scholar Award from the American Cancer Society. The award will fund research into potential therapies against pancreatic cancer, the third-leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States, which is forecast to become the second-leading cause by 2030. Read MoreSep 26, 2025
-
Researchers uncover critical genetic drivers of the gut’s “nervous system” development, offering insights into gut motility disorders
Vanderbilt researchers, including those from the Vanderbilt Brain Institute, have made significant strides in understanding how the enteric nervous system—sometimes called the “brain” of the gut—forms and functions. Read MoreSep 4, 2025
-

Engineering professor receives $3.1M NIH grant to develop augmented reality surgery system for precision cochlear implant procedures
Jack Noble, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering, is working with clinical colleagues to develop and validate an augmented reality vision guidance system to help surgeons place cochlear implants more precisely. The guidance system leverages emerging artificial intelligence technology and uses inexpensive, commonly available equipment, making it practical for many operating rooms. Read MoreAug 22, 2025
-
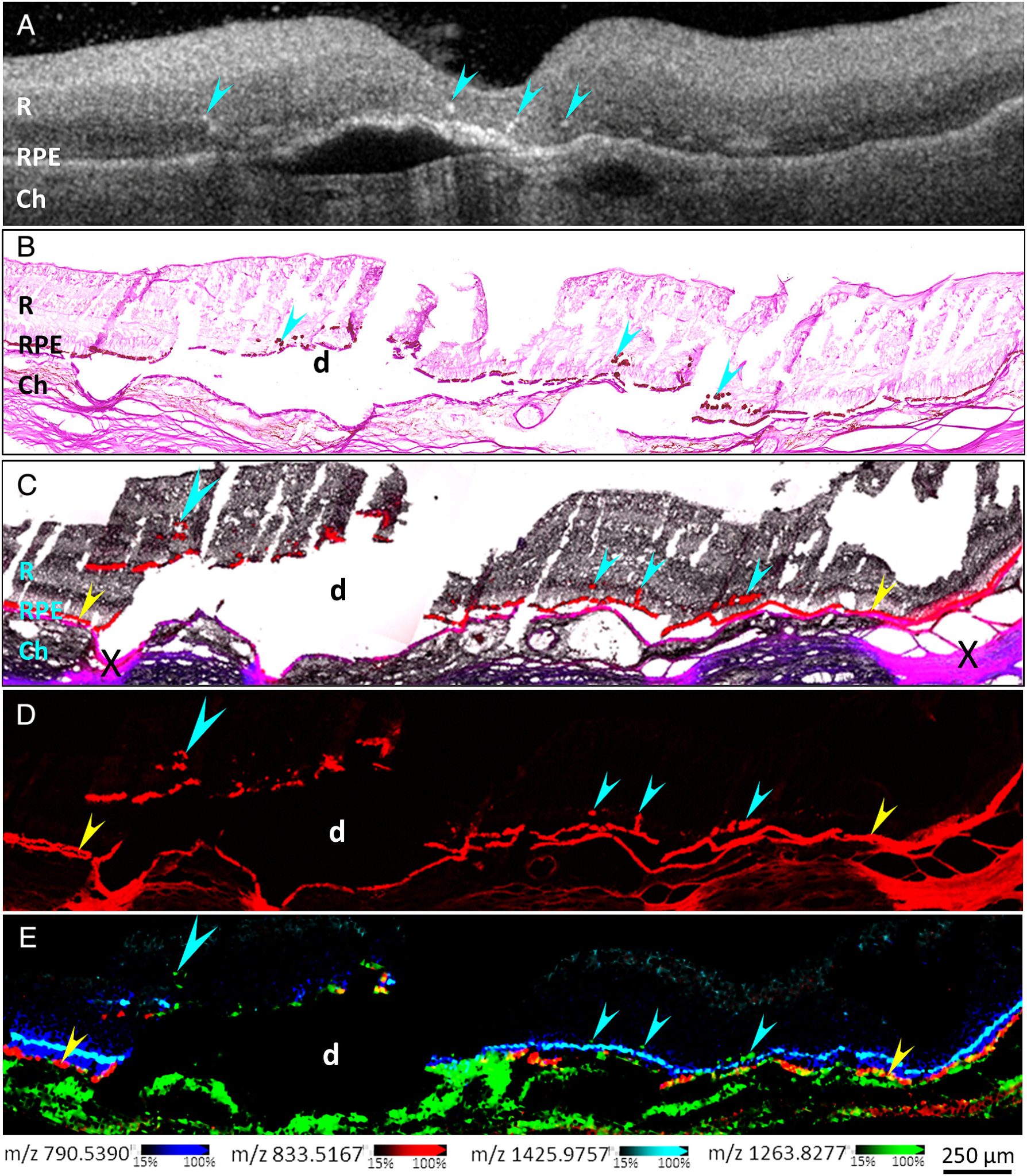
New research points to lipids as possible culprit in age-related vision loss
When we think of the age-old adage about getting old, “What new ache or pain will each new day bring?” we often imagine ailments such as joint or bone pain, a hyperactive bladder, or even memory loss, but Kevin Schey, Stevenson Professor of Biochemistry at the School of Medicine Basic Sciences, thinks a lot about the loss of eyesight. Read MoreAug 22, 2025
-
Metal and semiconductor particles could transform health and safety technologies
Ultra-thin layers of gold and copper sulfide developed by Vanderbilt doctoral student Yueming Yan with Associate Professor of Chemistry Janet Macdonald and Stevenson Professor of Physics Richard Haglund could revolutionize medical imaging and environmental sensing. The energy exchange between the metal and semiconductor particles—resonant energy transfer—can convert infrared light into visible and ultraviolet colors. The nanoscale films "could replace bulky optical sensors with flexible, wearable or even implantable devices, thus transforming health and safety technologies." Read MoreAug 7, 2025
-

Multicenter trial confirms near-infrared autofluorescence increases detection of parathyroid glands
The Vanderbilt Biophotonics Center, led by Professor Anita Mahadevan-Jansen, developed a device called the PTeye that can help surgeons see patients' parathyroid glands—which have unpredictable locations—better during neck surgery by making the tissue glow! A large, multicenter clinical trial has provided evidence of its effectiveness, which the team hopes will improve the accuracy of endocrine neck surgery and improve patient outcomes. Clinical implementation of the device was pioneered by Dr. Carmen Solórzano, director of Vanderbilt Endocrine Surgery at VUMC. Read MoreAug 7, 2025
-

New research points to cell subtypes that increase risk of diabetes
Three Vanderbilt faculty members are diving into a "chicken-and-egg" problem of type 2 diabetes: Does the disease change beta-cell subtypes? Or do changes in the cells cause diabetes? Guoqiang Gu, Emily Hodges and Ken Lau have come up with a new method of studying the subtypes that can track them through different stages instead of just once when they're fully developed. "Thanks to this and other research, it may be possible to one day create a diet supplement for pregnancy that could reduce the risk of diabetes for babies," Gu said. Read MoreAug 7, 2025
-
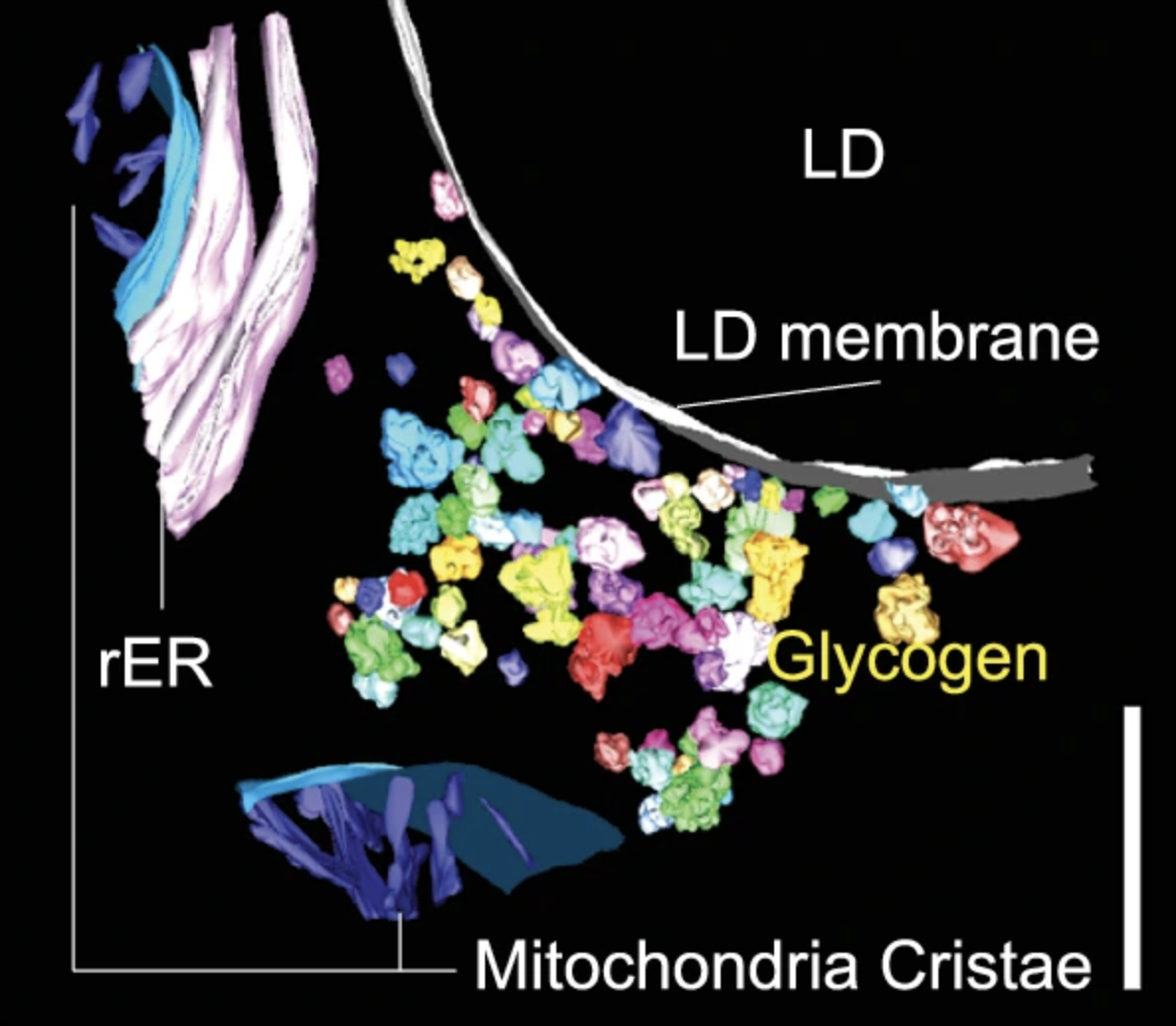
Pioneering new method reveals glucose channeling, charting the fine structure of energy metabolism inside active cells
In a scientific first, researchers from Vanderbilt University and the University of California, San Diego, have generated a high-resolution metabolic “map” of how cells orchestrate glucose processing, revealing a hidden world where organelles and molecular complexes collaborate when responding to a rush of nutrients. This new study, published in Nature Communications, has redefined how glucose metabolism is visualized at the single-cell level. Read MoreJul 21, 2025
-
Vanderbilt Memory and Alzheimer’s Center receives federal funding to support world-class research as a Center of Excellence
The announcement of the recognition of VMAC as an NIH Center of Excellence comes nearly five years after the creation of an exploratory NIA-funded Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center. Read MoreJul 21, 2025
-
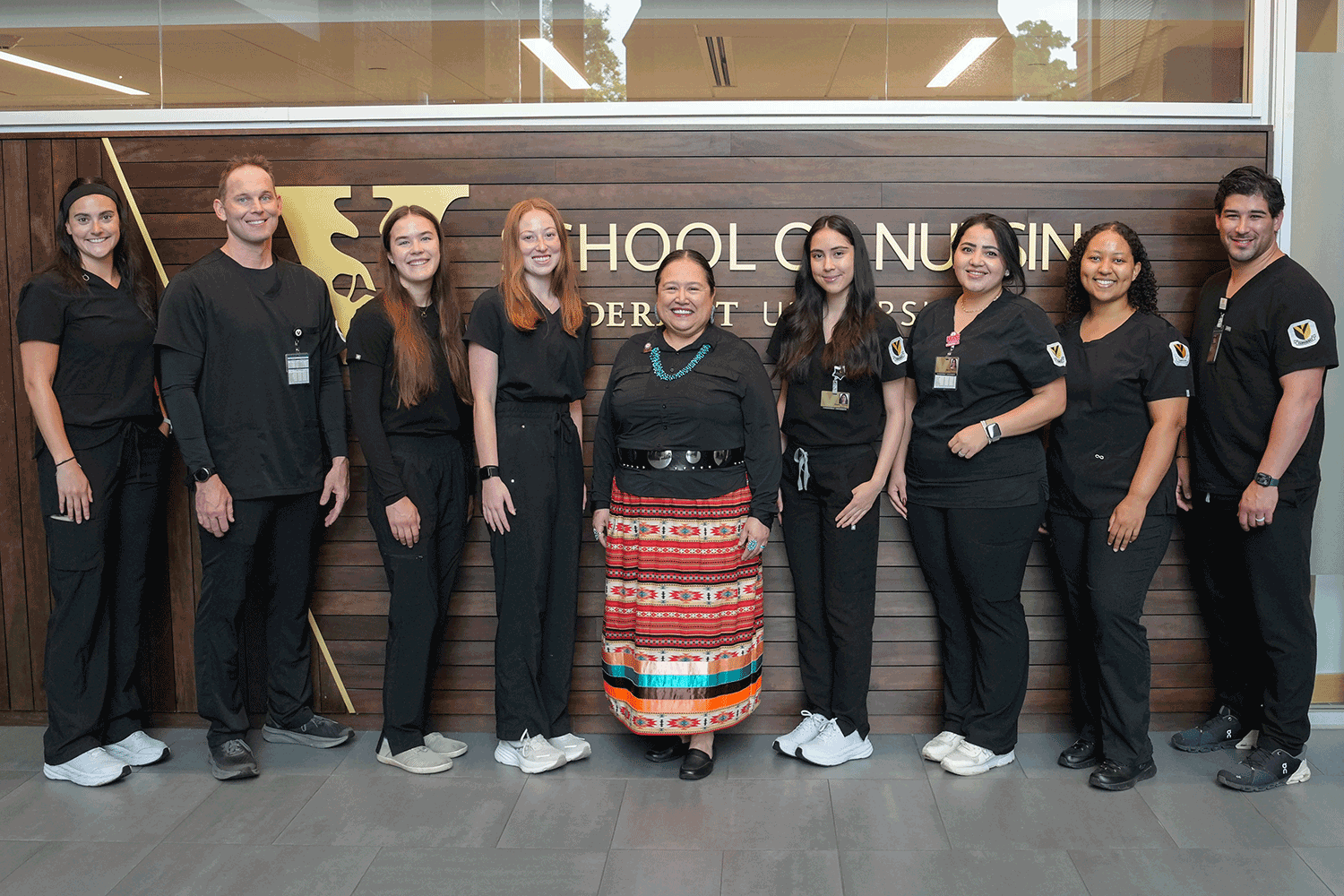

Bedford Falls Foundation funds innovative workforce retention pilot with School of Nursing
Vanderbilt University School of Nursing has received a $250,000 Innovation Grant from the Bedford Falls Foundation for a pilot program designed to equip nursing students and new registered nurses with tools that increase their job satisfaction so that they remain vitally needed members of the nursing workforce. The grant is the first awarded by the Bedford Falls Foundation. Read MoreJul 21, 2025
-
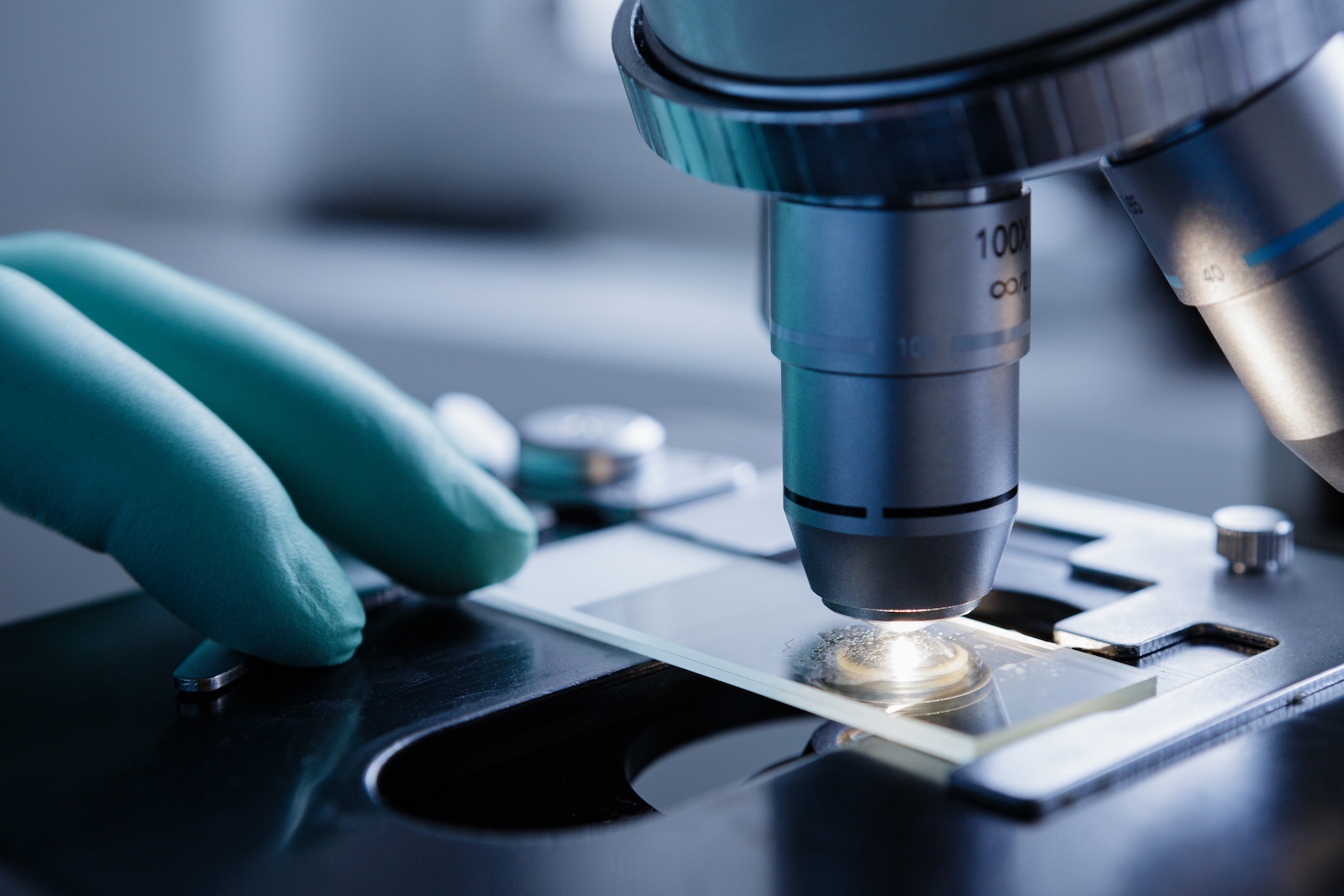

Researchers receive $1.2 million NSF grant to develop smart microscope system
Vanderbilt researchers have received a $1.2 million grant from the National Science Foundation to develop a smart microscope system that uses artificial intelligence to help scientists better understand how cells behave, particularly in diseases like cancer. Read MoreJul 17, 2025
-
Vanderbilt biologist receives $1.3M Keck grant to study what birds’ longevity could mean for human aging
Pet parrots often outlive their owners, and Vanderbilt researchers want to know why—because uncovering the biological mechanisms behind exceptional longevity could one day help safely extend the lives of humans. With the support of a new $1.3 million grant from the W.M. Keck Foundation, Vanderbilt biologist Gianni Castiglione is taking a bold approach to aging research: reverse-engineering how birds live three to four times longer than similarly sized mammals to identify safe, effective genetic targets for human aging therapies. Read MoreJul 16, 2025
-

Breakthrough study shows how brain-to-computer ‘electroceuticals’ can help restore cognition
Just like electrical stimulation of heart muscles can restore a regular heartbeat, new research led by Thilo Womelsdorf suggests that "electroceutical" intervention in the brain can improve memory and other cognitive functions wrought by behavioral health disorders and diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Womelsdorf, professor of psychology and biomedical engineering at the Vanderbilt Brain Institute, said, “For these cognitive disabilities, brain-computer interfaces promise to become next-generation electroceutical treatment options.” Read MoreJul 10, 2025
-

Nanobody hitchhikers boost immunotherapy potency in cancer treatment
A collaboration among VUMC, the College of Arts and Science, the School of Medicine and the School of Engineering has led to some higher-order “hitchhikers” that can make immunotherapy cancer treatments more effective. Associate Professor John Wilson’s lab devised a way to piggyback cancer-fighting nanobodies onto molecules that naturally accumulate around tumors—getting the treatment where it needs to go. Read MoreJul 10, 2025
-

Quynh Anh Nguyen awarded prestigious Klingenstein Fellowship to study mechanisms of epilepsy
Quynh Anh Nguyen, assistant professor of pharmacology, is the first Vanderbilt faculty member to be awarded the highly competitive Klingenstein Fellowship in Neuroscience since 1985. Her research aims to unravel the mysteries of epilepsy by focusing on how specific cells in the brain contribute to or suppress the hyperexcitability in neural circuits that are thought to be involved in the disorder’s spontaneous seizures. Read MoreJul 10, 2025
-

Vanderbilt researchers develop new approach to boost immunotherapy potency in cancer treatment
Researchers led by John T. Wilson, associate professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering and biomedical engineering, have developed a new approach using a molecularly designed nanobody platform that seeks to make immunotherapy more effective in the treatment of cancer. Read MoreJun 17, 2025
-

New research offers promise for treatment-resistant cystic fibrosis patients
A recent study from the labs of Lars Plate and Jens Meiler, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, analyzed both selectively responsive and poorly responsive variants of cystic fibrosis and revealed the molecular determinants of drug response. Read MoreJun 12, 2025
-

A Package Deal: Diagnosing and treating breast cancer with a single complex
A group of researchers from the lab of Larry Marnett, the Mary Geddes Stahlman Professor of Cancer Research, recently paired a precisely targeted imaging agent to an anticancer agent and found that they could specifically attack cancer cells and not normal cells with it. Their work was performed in collaboration with School of Engineering faculty members Craig Duvall and Rebecca Cook, and was published in Molecular Pharmaceutics in April 2025. Read MoreJun 12, 2025
-

New ketamine study promises extended relief for depression
In a new study published in Science, Lisa Monteggia’s and Ege Kavalali’s labs show that it is feasible to substantially extend the efficacy of a single dose of ketamine from its current duration of up to a week to a longer period of up to two months. Read MoreJun 12, 2025